As global livestock production continues to evolve under increasing regulatory, sustainability and economic pressures, interest in plant-based products with a long history of use and strong scientific support is steadily growing. Among these, Macleaya cordata (plume poppy) stands out as a botanical species rooted in traditional use and increasingly explored within modern animal production research.
Macleaya cordata is a well-documented plant in traditional herbal medicine, with recorded use dating back several centuries. The species is native to China, and even today it remains the principal source of Macleaya cordata raw materials, supported by established agricultural production systems and botanical expertise.
This historical background has laid the foundation for modern scientific exploration, allowing researchers to bridge traditional knowledge with modern analytical and molecular tools.
From plant production to scientific standardisation
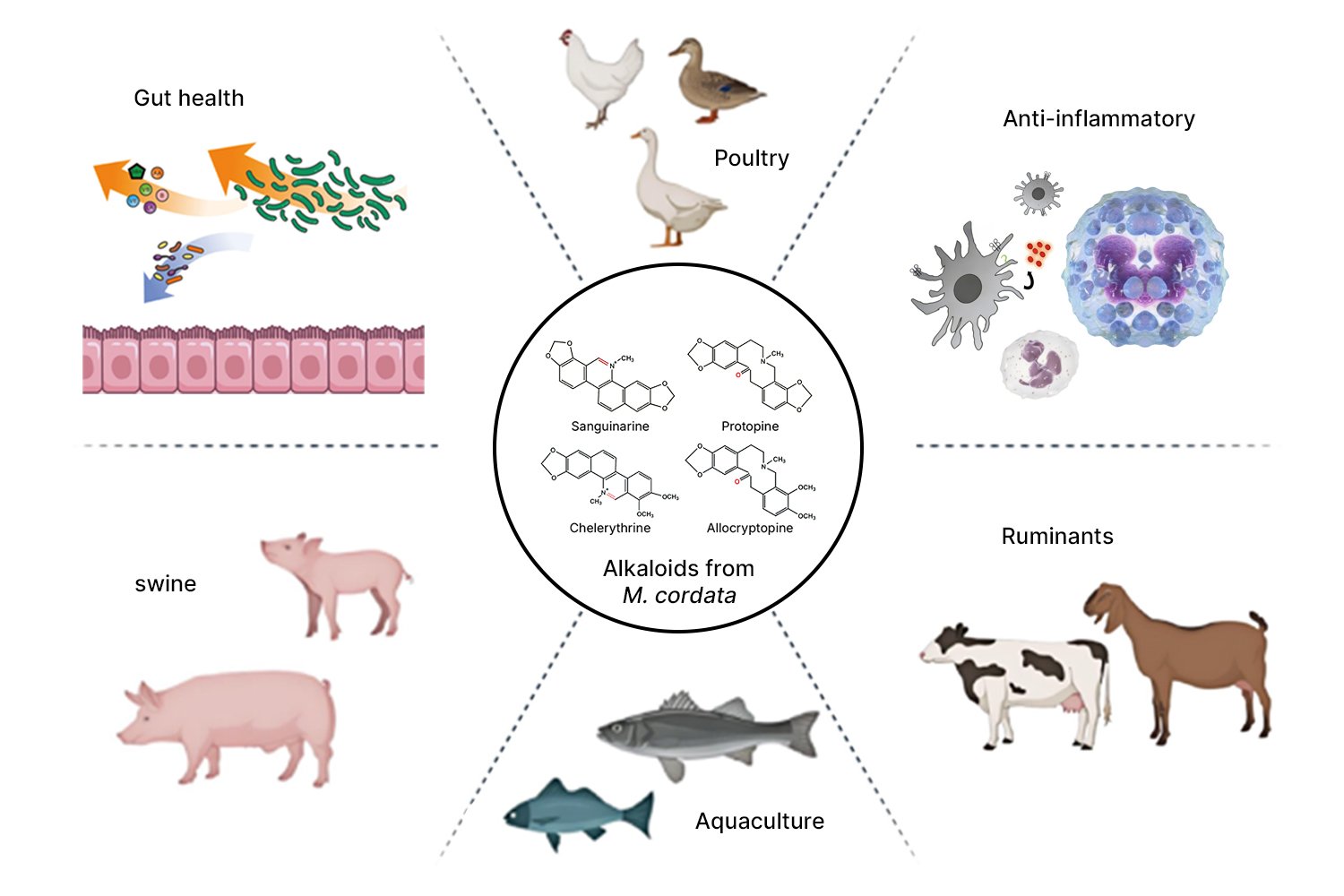
Interest in Macleaya cordata in the context of animal production research is closely linked to advances in plant cultivation, processing and standardisation. The plant contains naturally occurring isoquinoline alkaloids, particularly sanguinarine and chelerythrine, which have been widely investigated in biochemical and physiological studies.
Modern production approaches increasingly focus on controlled cultivation, genetic selection and breeding, traceability of raw materials and consistent phytochemical profiles. To support these objectives, VTR Biotech has established a Macleaya cordata germplasm bank over the past decade and developed a standardised cultivation system. The company operates approximately 3,400 hectares of organically certified cultivation areas, representing one of the largest integrated production bases for Macleaya cordata and supporting a stable supply of plant material.
Scientific attention in animal production research
Over the past 2 decades, Macleaya cordata has become a subject of interest in animal production research across multiple species. Academic studies have explored its association with intestinal environments, microbial ecosystems, oxidative balance and immune-related pathways, contributing to a broader understanding of how plant-derived compounds interact with animal physiology at molecular and systemic levels.
Importantly, this research focus is largely embedded within broader discussions on sustainable production, reduced reliance on conventional inputs, alongside its anti-inflammation and growth-promoting effects.
VTR Biotech and Micolta: advancing global research leadership
Within this research landscape, VTR Biotech and its subsidiary Micolta have played a central role in advancing scientific understanding of Macleaya cordata. Through sustained investment in botanical research, the group has contributed to a substantial number of peer-reviewed publications addressing plant genomics, bioactive compound biosynthesis and interactions with animal biological systems.
Research has been published in global leading journals such as Molecular Plant, Microbiome and Phytotherapy Research, highlighting its academic significance. Rather than focusing on isolated outcomes, these studies aim to clarify underlying mechanisms at molecular, microbial and systemic levels, providing a robust scientific framework for future applications.

A notable milestone has been the complete mapping of the Macleaya cordata genome, and the revealing of the molecular mechanisms of bio-alkaloid biosynthesis, storage, and transport pathways, opening up new perspectives for innovative plant utilisation in animal production.
Looking ahead: integrating botanical science into European animal production
As European animal production continues to explore research-driven and sustainable approaches, botanically-derived products with strong scientific foundations are attracting growing interest. In this context, VTR Biotech’s European subsidiary, Vnzymes (Victory Enzymes GmbH), is positioned to play a strategic role by integrating the group’s advancing expertise and Macleaya cordata resources with local market knowledge and regulatory frameworks.
By combining traditional botanical heritage, modern plant science and international collaboration, Macleaya cordata represents a compelling example of how ancient plants can inform innovative, future-oriented animal production systems.